Performance Analysis of AutoDist¶
The primary motivation of AutoDist is to build a scalable ML engine for distributed TensorFlow model training. AutoDist provides different distributed training strategies, incuding some of the latest distributed strategies. In order to report the performance of AutoDist for different strategies across different deep learning models, we benchmark its performance with Tensorflow and a state-of-the-art distributed training framework.
Experiment Setup¶
Dataset and Model¶
We benchmark AutoDist with Horovod on the dataset of ImageNet across ResNet101, DenseNet121, InceptionV3 and VGG16, which are four state-of-the-arts convolutional neural networks, and also on a sample dataset for pre-training the BERT-large, uncased model (https://github.com/google-research/bert). Our experiments were done with at most sixteen AWS server instances with type g4dn.12xlarge which have 4 NVIDIA T4 GPUs each connected by a 50 Gbit/s network. In order to show the performance under different scale of GPUs, we respectively perform experiments with one server, two servers, four servers, eight servers and sixteen servers. All the experiments were performed in Tensorflow 2.0.1 with CUDA 10.0.130 and CUDNN 7.6.5. AutoDist and Horovod were run in the exact same environment and setting of instances.
Strategy Configuration¶
In AutoDist, we include five distributed strategies: PS, PartitionedPS, PSLoadBalancing, AllReduce and Parallax. For AllReduce and Parallax, we use the Ring-based AllReduce algorithm. The code we use for running AutoDist on these experiments can be viewed here.
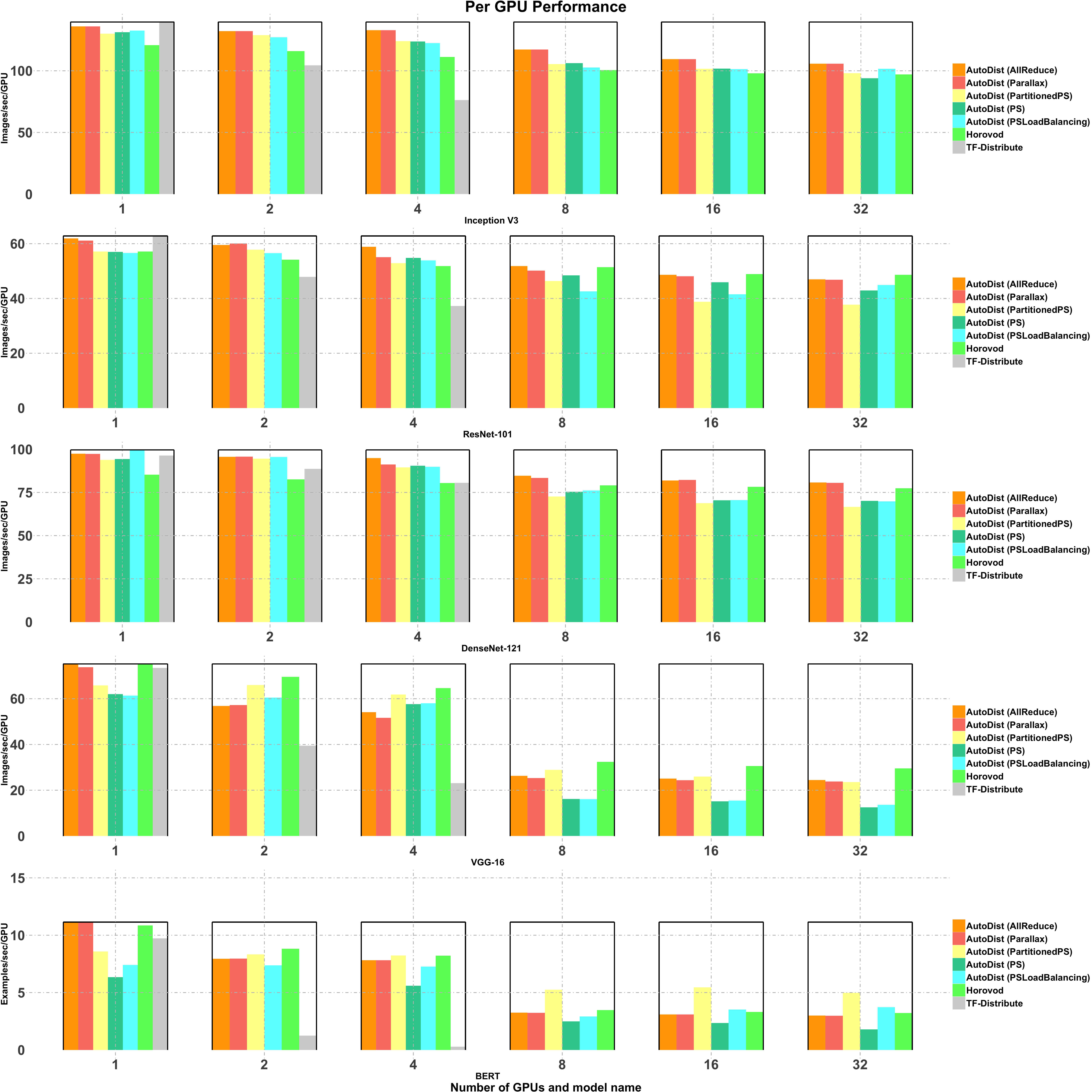
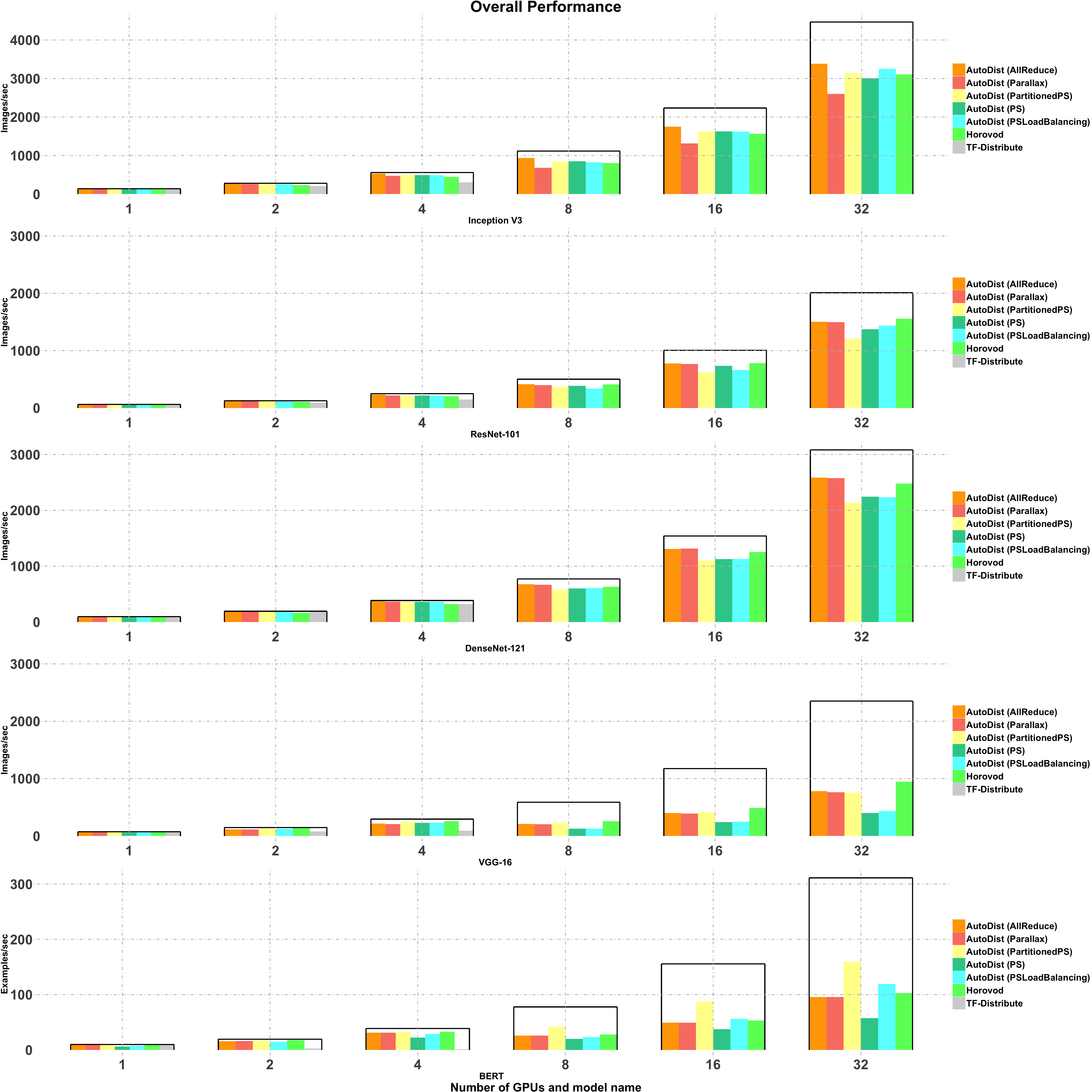
Performance Comparison¶
The performance comparison is summarized in the figure below. It shows that different models achieve the best performance with different AutoDist strategies. The performance per GPU is stable with different numbers of GPUs used, which suggests AutoDist has good scalability with increased GPUs.